Hadoop - HDFS Architecture
NameNode and DataNodes
HDFS has a master/slave architecture. An HDFS cluster consists of a single NameNode, a master server that manages the file system namespace and regulates access to files by clients. In addition, there are a number of DataNodes, usually one per node in the cluster, which manage storage attached to the nodes that they run on. HDFS exposes a file system namespace and allows user data to be stored in files. Internally, a file is split into one or more blocks and these blocks are stored in a set of DataNodes. The NameNode executes file system namespace operations like opening, closing, and renaming files and directories. It also determines the mapping of blocks to DataNodes. The DataNodes are responsible for serving read and write requests from the file system’s clients. The DataNodes also perform block creation, deletion, and replication upon instruction from the NameNode,More info go through hadoop admin course
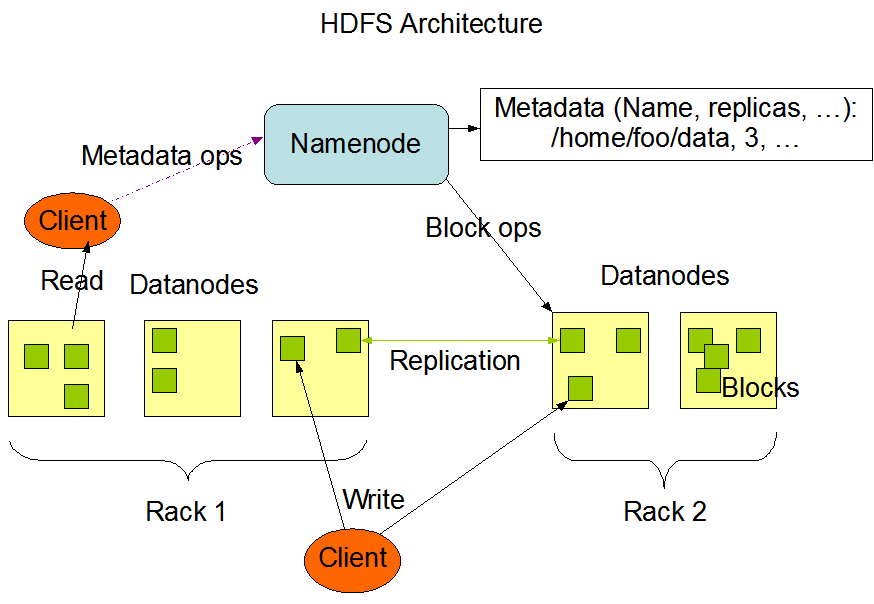
The DataNode are pieces of software designed to run on commodity machines and Name Node run on High Availability Hardware. These machines typically run a GNU/Linux operating system (OS). HDFS is built using the Java language; any machine that supports Java can run the NameNode or the DataNode software. Usage of the highly portable Java language means that HDFS can be deployed on a wide range of machines. A typical deployment has a dedicated machine that runs only the NameNode software. Each of the other machines in the cluster runs one instance of the DataNode software. The architecture does not preclude running multiple DataNodes on the same machine but in a real deployment that is rarely the case.
The existence of a single NameNode in a cluster greatly simplifies the architecture of the system. The NameNode is the arbitrator and repository for all HDFS metadata. The system is designed in such a way that user data never flows through the NameNode.
The File System Namespace
HDFS supports a traditional hierarchical file organization. A user or an application can create directories and store files inside these directories. The file system namespace hierarchy is similar to most other existing file systems; one can create and remove files, move a file from one directory to another, or rename a file. HDFS does not yet implement user quotas. HDFS does not support hard links or soft links. However, the HDFS architecture does not preclude implementing these features.
The NameNode maintains the file system namespace. Any change to the file system namespace or its properties is recorded by the NameNode. An application can specify the number of replicas of a file that should be maintained by HDFS. The number of copies of a file is called the replication factor of that file. This information is stored by the NameNode.
Data Replication
HDFS is designed to reliably store very large files across machines in a large cluster. It stores each file as a sequence of blocks; all blocks in a file except the last block are the same size. The blocks of a file are replicated for fault tolerance. The block size and replication factor are configurable per file. An application can specify the number of replicas of a file. The replication factor can be specified at file creation time and can be changed later. Files in HDFS are write-once and have strictly one writer at any time.
The NameNode makes all decisions regarding replication of blocks. It periodically receives a Heartbeat and a Blockreport from each of the DataNodes in the cluster. Receipt of a Heartbeat implies that the DataNode is functioning properly. A Blockreport contains a list of all blocks on a DataNode.

Replica Placement: The First Baby Steps
The placement of replicas is critical to HDFS reliability and performance. Optimizing replica placement distinguishes HDFS from most other distributed file systems. This is a feature that needs lots of tuning and experience. The purpose of a rack-aware replica placement policy is to improve data reliability, availability, and network bandwidth utilization. The current implementation for the replica placement policy is a first effort in this direction. The short-term goals of implementing this policy are to validate it on production systems, learn more about its behavior, and build a foundation to test and research more sophisticated policies.
Large HDFS instances run on a cluster of computers that commonly spread across many racks. Communication between two nodes in different racks has to go through switches. In most cases, network bandwidth between machines in the same rack is greater than network bandwidth between machines in different racks.
The NameNode determines the rack id each DataNode belongs to via the process outlined in Hadoop Rack Awareness. A simple but non-optimal policy is to place replicas on unique racks. This prevents losing data when an entire rack fails and allows use of bandwidth from multiple racks when reading data. This policy evenly distributes replicas in the cluster which makes it easy to balance load on component failure. However, this policy increases the cost of writes because a write needs to transfer blocks to multiple racks.
For the common case, when the replication factor is three, HDFS’s placement policy is to put one replica on one node in the local rack, another on a node in a different (remote) rack, and the last on a different node in the same remote rack. This policy cuts the inter-rack write traffic which generally improves write performance. The chance of rack failure is far less than that of node failure; this policy does not impact data reliability and availability guarantees. However, it does reduce the aggregate network bandwidth used when reading data since a block is placed in only two unique racks rather than three. With this policy, the replicas of a file do not evenly distribute across the racks. One third of replicas are on one node, two thirds of replicas are on one rack, and the other third are evenly distributed across the remaining racks. This policy improves write performance without compromising data reliability or read performance.
The current, default replica placement policy described here is a work in progress.
Replica Selection
To minimize global bandwidth consumption and read latency, HDFS tries to satisfy a read request from a replica that is closest to the reader. If there exists a replica on the same rack as the reader node, then that replica is preferred to satisfy the read request. If angg/ HDFS cluster spans multiple data centers, then a replica that is resident in the local data center is preferred over any remote replica.
Safemode
On startup, the NameNode enters a special state called Safemode. Replication of data blocks does not occur when the NameNode is in the Safemode state. The NameNode receives Heartbeat and Blockreport messages from the DataNodes. A Blockreport contains the list of data blocks that a DataNode is hosting. Each block has a specified minimum number of replicas. A block is considered safely replicated when the minimum number of replicas of that data block has checked in with the NameNode. After a configurable percentage of safely replicated data blocks checks in with the NameNode (plus an additional 30 seconds), the NameNode exits the Safemode state. It then determines the list of data blocks (if any) that still have fewer than the specified number of replicas. The NameNode then replicates these blocks to other DataNodes.
The Persistence of File System Metadata
The HDFS namespace is stored by the NameNode. The NameNode uses a transaction log called the EditLog to persistently record every change that occurs to file system metadata. For example, creating a new file in HDFS causes the NameNode to insert a record into the EditLog indicating this. Similarly, changing the replication factor of a file causes a new record to be inserted into the EditLog. The NameNode uses a file in its local host OS file system to store the EditLog. The entire file system namespace, including the mapping of blocks to files and file system properties, is stored in a file called the FsImage. The FsImage is stored as a file in the NameNode’s local file system too.
The NameNode keeps an image of the entire file system namespace and file Blockmap in memory. This key metadata item is designed to be compact, such that a NameNode with 4 GB of RAM is plenty to support a huge number of files and directories. When the NameNode starts up, it reads the FsImage and EditLog from disk, applies all the transactions from the EditLog to the in-memory representation of the FsImage, and flushes out this new version into a new FsImage on disk. It can then truncate the old EditLog because its transactions have been applied to the persistent FsImage. This process is called a checkpoint. In the current implementation, a checkpoint only occurs when the NameNode starts up. Work is in progress to support periodic checkpointing in the near future.
The DataNode stores HDFS data in files in its local file system. The DataNode has no knowledge about HDFS files. It stores each block of HDFS data in a separate file in its local file system. The DataNode does not create all files in the same directory. Instead, it uses a heuristic to determine the optimal number of files per directory and creates subdirectories appropriately. It is not optimal to create all local files in the same directory because the local file system might not be able to efficiently support a huge number of files in a single directory. When a DataNode starts up, it scans through its local file system, generates a list of all HDFS data blocks that correspond to each of these local files and sends this report to the NameNode: this is the Blockreport.
The Communication Protocols
All HDFS communication protocols are layered on top of the TCP/IP protocol. A client establishes a connection to a configurable TCP port on the NameNode machine. It talks the ClientProtocol with the NameNode. The DataNodes talk to the NameNode using the DataNode Protocol. A Remote Procedure Call (RPC) abstraction wraps both the Client Protocol and the DataNode Protocol. By design, the NameNode never initiates any RPCs. Instead, it only responds to RPC requests issued by DataNodes or clients.
To learn complete Course visit ITGuru's hadoop administration course



No comments: